Factoring trinomials worksheet (solved examples)
Factorise the following Quadratic trinomials 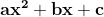 by spiliting the middle terms.
by spiliting the middle terms.
| We know, in order to factorise the expression ax2 + bx + c, we have to find two numbers p and q, such that p + q = b and p × q = ac. |
Example 1: Factorise
Solution. Find two factors p and q such that p+q=-7 and pq =12 . Take p=-3 and q=-4 then 12= -3 x (-4) and -3-4=-7 .
Therefore =
=
=
=
Example 2: Obtain the factors of .
Solution. =
=
=
Example 3: Find the factors of .
Solution. Note that 3 is common factor in all the terms. Therefore
=
=
=
=
Example 4: Factorise .
Solution. We split into two parts whose sum is
and product is 12. Clearly
and
=
=
Hence =
Example 5: Factorise .
Sol. Here , 9 x 8 =72. We spilt -22 into parts whose sum is-22 and product 72 .
Clearly , (-18)+(-4) =-22 and (-18) x (-4)=72 .
=
=
Hence =
Example 6: Factorise .
Sol. Here , . We spilt -47 into two parts whose sum is-47 and product 90 .
Clearly , (-2)+(-45) =-47 and (-2) x (-45)=90 .
=
=
Hence =
.
Example 7: Factorise .
Solution : Here, . We split
into two parts whose sum is
and product
.
Clearly, and
.
=
=
=
Hence =
.
Example 8: Factorise .
Solution: The given expression is .
Here , .
So, we split -10 in two parts whose sum is -10 and product -56.
Clearly, (-14+4) =-10 and (-14) x 4 =-56.
=
=
=
Factoring trinomials worksheet PDF download
You might also be interested in:
- Polynomials : Definition, Types of polynomials and Examples, Degree of a polynomial
- Relationship between Zeros and coefficients of a Polynomial
- Polynomials Worksheet Grade 9 with PDF
- Factoring Polynomials Formula and Factoring Polynomials Worksheet with Answers
